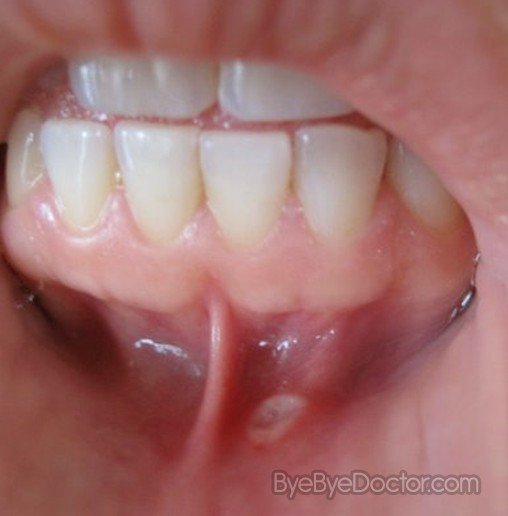
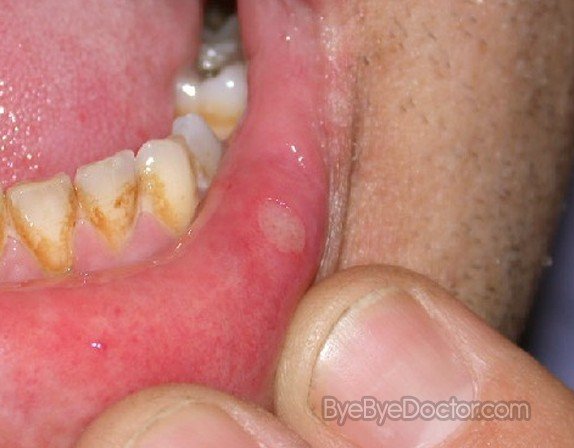
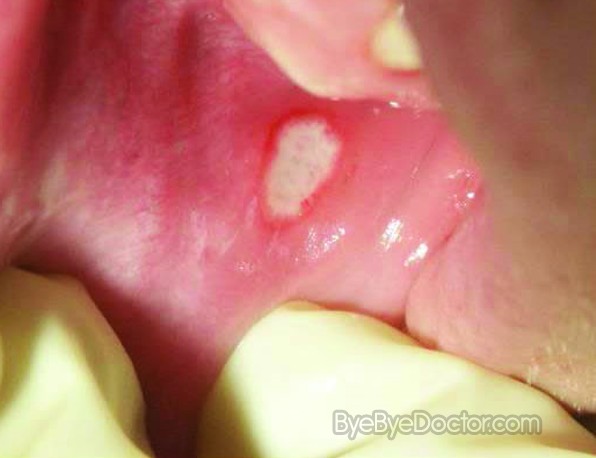
What is a Canker sore?
Canker sores are also known as apthous ulcers and are shallow small lesions which develop on the tissues in the mouth which are soft as well as the bottom of the gums. Different from cold sores, these sores do not happen on the surface of the lips and are not contagious. But they are often exceptionally painful and therefore can make talking as well as eating trying.
Canker Sore Causes
Causes for canker sores include:
- Food allergies
- A diet lacking in zinc, foliate, iron or vitamin B-12
- Allergic responses to certain bacteria in the mouth
- Helicobacter pylon, the same bacteria causing peptic ulcers
- Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- Celiac disease which is an intestinal condition caused by a sensitivity to gluten which is a protein found in most grains.
- Behcet’s disease which is a rare condition that causes inflammation thru out the body including the mouth.
- HIV/AIDS which suppresses the immune system
- Faulty immune system which attacks healthy cells in the mouth instead of pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria
- Emotional stress
- Hormonal shifts during menstruation
- Toothpastes and mouth rinses which contain sodium lauryl sulfate
Canker Sore Symptoms
The majority of canker sores are oval or round with a yellow or white center and a red border. They form inside the mouth – on or under the tongue, inside the cheeks or lips as well as the base of the gums. An individual might notice a burning or tingling sensation a day or two before the sores actually appear.
Minor canker sores – These most common canker sores:
- Are less than about ½ inch in diameter
- Are oval shaped
- Heal without scarring in 1 to 2 weeks
Major canker sores – These less common sores:
- Are greater than about ½ inch in diameter
- Have edges which are irregular
- May take up to 6 weeks to heal as well as leave extensive scarring
Herpetiform canker sores – These sores, which normally develop late in life:
- Are each no bigger than 1/8 inch
- Often develop in clusters of 10 to 100 sores
- Have edges which are irregular
- Heal without scarring in 1 to 2 weeks
Additional symptoms
Occasionally, an individual may experience other symptoms or signs along with the lesions, such as:
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Listlessness
An individual should see their physician if they experience any of the following:
- Unusually large sores
- Recurring ulcers with new ones developing before old ones heal
- Sore which extend into the lip themselves
- Persistent sores lasting 3 weeks or more
- Extreme problems with drinking or eating
- Pain that can not be control with self-care measures
- High fever along with canker sores
Any individual can cultivate canker sores, but these influences below do make a person more vulnerable:
Females
These sores particularly ones that grow in clusters of small lesions, are most common in females.
Family history
Approximately 1/3 of individuals with recurring canker sores have a history of this condition in their family. This could be due to genetics or to a collective influence in the environment such as allergens or certain foods.
Canker Sore Treatment
Treatment normally is not required for minor canker sores, as they have a tendency to clear on by themselves in a few weeks. But persistent, large or abnormally aching lesions need remedial care. A quantity of different treatment preferences exists and they range from topical ointments and mouth rinses to general oral corticosteroids for individual cases which are most severe.
http://www.Symptoms-Causes-treatment.blogspot.com detect diseases at an early stage symptoms, and find out the causes and treatments best suited.
Rinses for the Mouth
If individuals who have a large amount of sores, a physician may recommend a mouth rinse that contains the steroid dexamethasone which reduces inflammation as well as pain. Oral liquids of antibiotics such as tetracycline can also decrease pain as well as reduce healing time. It can cause the individual to be more vulnerable to oral thrush which is a fungal infection causing throbbing lesions in the mouth and can lastingly stain the teeth in children.
Topical Pastes
Prescription as well as OTC pastes with ingredients such as amlexanox (Aphthasol), benzocaine (Orabase), as well as fluocinonide (Vanos, Lidex) may help with the relieve of pain as well as hurry healing if put on individual sores immediately as they develop.
Medications Oral
Drugs which are not intended precisely for the management of canker sores, such as heartburn medication cimetidine (Tagamet) and colchicine, normally used for the treatment of gout, can be helpful with canker lesions. Oral steroid drugs are also occasionally given when canker sores are severe and do not respond to any additional treatments. However these are normally considered a last resort treatment because of the side effects of steroids.
Debacterol
This is a topical solution specifically developed to manage canker sores and gum difficulties. By the chemical cauterizing of lesions, it can reduce the healing time to around a week.
Nutritional Supplements
The doctor is probably to recommend a nutritional supplement if the individual consumes small quantities of essential nutrients such as folic acid, vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, as well as zinc.
Other Disorders
If the canker sores appear to be linked to a more severe problem with health, the doctor will treat the primary disorder.
Canker Sore Home Remedies
- Rinse mouth – Using salt water; hydrogen peroxide weakened in half with water; or mix 1 part Benadryl with either 1 Kaopectate or 1 part Maalox; or baking soda (dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda with one-half cup of water which is warm).
- Coat sores with paste made with baking soda.
- Use OTC medications which have a numbing ingredient such as Orajel and Anbesol
- Evade coarse, spicy or acidic foods which can cause additional pain and irritation
- Hold ice to canker sores or permit chips of ice to gradually melt over the lesions.
- Brush teeth softly using a brush which is soft with toothpaste lacking any foaming ingredient for instance TheraBreath.
Canker Sore Pictures